In the ever-evolving landscape of natural language processing and artificial intelligence, new techniques and models are constantly emerging to enhance the way we generate and interact with text. One such advancement is Retrieval Augmented Generation, a technology that’s changing the way we approach content generation and information retrieval.
What is Retrieval Augmented Generation?
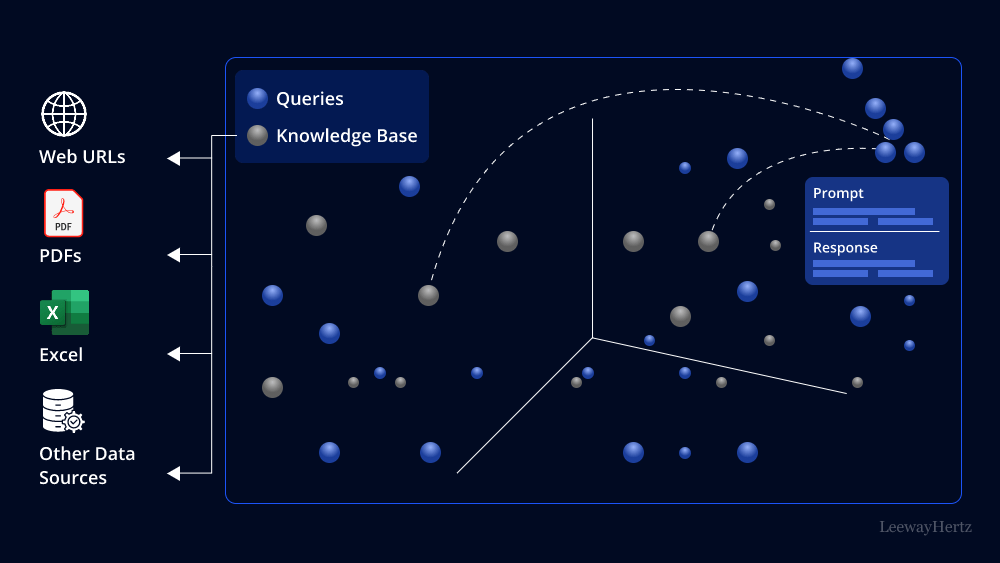
Retrieval Augmented Generation, often abbreviated as RAG, is a groundbreaking AI methodology that marries the strengths of retrieval and generation models. It bridges the gap between traditional search engines and natural language generation, offering a unique solution to information retrieval and content creation challenges.
The concept of RAG is elegantly simple: it integrates retrieval-based and generation-based models into a single framework. Retrieval models are skilled at identifying relevant information in vast datasets, while generation models excel at creating human-like text. By combining these two approaches, RAG empowers machines to generate contextually rich, coherent, and informative content.
How Does Retrieval Augmented Generation Work?
RAG operates by using a retrieval model to identify potentially relevant passages from a vast corpus of text. It then employs a generation model to transform these passages into coherent and contextually relevant responses. This two-step process ensures that the generated content is not only informative but also coherent and contextually accurate.
The key components of RAG are as follows:
- Retriever: The retriever is responsible for searching through extensive datasets to identify relevant information based on a given query. It employs techniques like BM25 or neural retrievers to rank and select relevant passages.
- Generator: The generator takes the retrieved passages and creates coherent responses. It typically utilizes large language models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) to generate human-like text.
- Ranker (Optional): In some RAG architectures, a ranker model is employed to further filter and rank retrieved passages before they are passed to the generator. This step can help improve the quality of the generated content.
Applications of Retrieval Augmented Generation
The applications of Retrieval Augmented Generation are vast and diverse:
- Question Answering: RAG can answer questions by retrieving and generating answers from a knowledge base.
- Content Creation: It can assist content creators by suggesting contextually relevant information and even drafting entire articles or reports.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: RAG-powered chatbots can provide more accurate and context-aware responses, enhancing the user experience.
- Language Translation: RAG can be used to generate translations that are not only accurate but also contextually relevant.
- Enhancing Search Engines: Search engines can benefit from RAG by providing more accurate and informative search results.
Challenges and Future Developments
While Retrieval Augmented Generation has made significant strides in improving content generation and information retrieval, it’s not without its challenges. Fine-tuning the balance between retrieval and generation, managing computational resources, and addressing ethical considerations are some of the hurdles that researchers and developers continue to work on.
In the future, we can expect even more refined RAG models, improved algorithms, and wider adoption of this technology across various industries.
Conclusion
Retrieval Augmented Generation is a transformative technology that’s reshaping the way we access and create content. By merging the strengths of retrieval and generation models, RAG offers a unique solution to many information-related challenges. As the field continues to evolve, we can anticipate a world where content creation and retrieval are more efficient, accurate, and contextually relevant than ever before.
Source Url: https://www.leewayhertz.com/what-is-retrieval-augmented-generation/